The Ripple Effect of Sustaining Innovation: How Marginal Innovations Compound Over Time
Innovation serves as the catalyst for progress, growth, and competitive advantage. Among the diverse approaches, sustaining innovation stands out as a powerful force that drives incremental advancements in existing products, services, and processes—doing what already sets you apart, but better. Often perceived as modest and marginal, these sustained improvements can create ripple effects that resonate far beyond their initial impact.
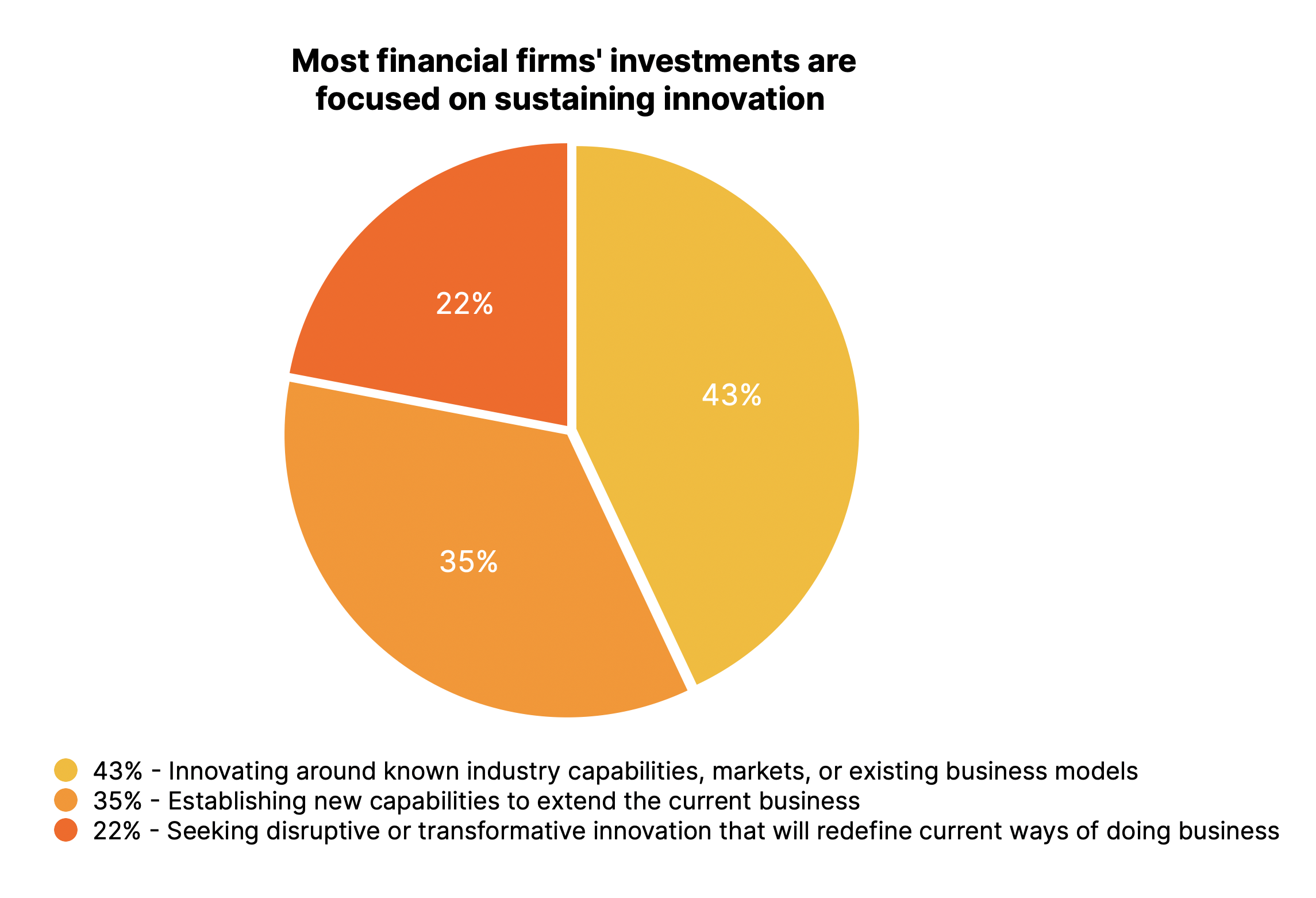
In this article, we delve into the fascinating concept of the ripple effect of sustaining innovation, exploring how seemingly minor innovations can compound over time to yield substantial and transformative outcomes, resulting in a future of continuous improvement and long-lasting success.
Defining Sustaining and Disruptive Innovation
Sustaining innovation refers to incremental improvements and optimizations to something that already exists. The primary goal here is to enhance the value proposition for current clients, retain market share, and keep up with evolving customer needs. Sustaining innovation also involves refining features, enhancing performance, improving productivity, reducing costs, and streamlining operations.
Disruptive innovation, on the other hand, refers to the introduction of entirely new products or services that fundamentally change the existing market landscape. These innovations often cater to a previously underserved market segment and may initially be perceived as inferior by mainstream customers. However, disruptive innovations eventually improve and surpass existing offerings, leading to a radical shift in the industry.
While sustaining innovation targets existing customers, disruptive innovation creates new markets and customer segments.
How Does This Difference Look in Practice?
Deloitte’s Peter Capozucca broadly categorized the advantages of these two types into cost leadership, quality/performance, and speed-to-market.
Cost Leadership
In the telco industry, calling cards represented a sustaining innovation that made long-distance and international calls more convenient. Having streamlined the process and provided a cost-effective option, calling card sellers improved overall customer experience within the existing market framework.
However, messengers such as WhatsApp were disruptive and redefined the cost equation for telecommunications as a whole. Internet telephony leverages the power of the global web to transmit voice calls, bypassing traditional networks and significantly reducing costs. This transformative innovation has created a new market, catering to tech-savvy users seeking more economical and efficient communication solutions.
Quality/Performance
Think of compact fluorescent light bulbs (CFLs)—at the time, they brought an incremental improvement over traditional bulbs, offering higher energy efficiency. This sustaining innovation appealed to environmentally conscious consumers and those seeking energy-saving alternatives.
In contrast, light-emitting diode (LED) bulbs took the level of sustaining even higher. These bulbs proved more energy-efficient than CFLs, providing superior illumination quality, a longer lifespan, cooler operation, and contained no hazardous substances like mercury.
Speed-to-Market
Back in the day, DVD-by-mail emerged as a disruptive innovation, creating a new channel for movie distribution and increasing competitive pressures on local video stores. This innovation allowed customers to conveniently access a vast library of movies from their homes.
However, on-demand streaming video platforms like Netflix emerged as a more recent disruptive innovation, challenging the dominance of DVD-by-mail and traditional video stores. The advent of high-speed Internet connections enabled seamless and instant availability of various movies and TV shows. This transformation in video distribution highlights the importance of speed-to-market in capturing and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
The Ripple Effect of Sustaining Innovation
Publix Super Markets is a grocery store chain based in the southeastern U.S. It is not as widely known as some of its big-name competitors like Walmart or Kroger, but it has been highly successful in the regional market—to the extent it was named ‘Every Floridian’s Favorite Supermarket’ by Harvard.
Publix has definitely benefited from marginal innovations compounding over time. Its data-driven inventory optimization reduced excess stock and improved cash flow. At the same time, investments in supply chain optimization and employee training have allowed Publix to enhance efficiency and customer service, while adoption of energy-saving measures like LED lighting and HVAC systems (which were breakthrough at the time) lowered utility costs.
Interesting fact: back in 2001, Publix ventured into grocery delivery, but unfortunately, the service was ahead of its time and did not yield the desired results so the company shut it down. Despite this setback, Publix’s innovative spirit persisted, and over time, it continued to explore and adopt strategies other than disruptive innovation, which aligned better with market demands and tech advancements. The company’s culture of continuous improvement allowed for consistent small adjustments that collectively had a substantial impact on the bottom line.
The impact of sustaining innovation may not be immediately apparent, but its influence extends far beyond the surface. Much like a pebble dropped in a pond, the ripples of sustaining innovation spread throughout the organization and industry, leading to several noteworthy outcomes.
Customer Loyalty and Satisfaction
Sustaining innovation is customer-centric, aiming to meet and exceed expectations consistently. Continuous enhancement of products and services allows companies to bolster loyalty and satisfaction rates. When satisfied, customers tend to remain loyal to a brand and become advocates, thus contributing to a positive reputation and fostering increased customer retention.
Process Optimization and Efficiency
Sustaining innovation often involves streamlining internal processes, optimizing supply chains, and reducing waste. These efficiency improvements not only result in cost savings but also enable companies to redirect resources toward more substantial disruptive initiatives.
Learning and Adaptation
Sustaining innovation encourages a culture of learning and adaptation (more on that below). Organizations that embrace incremental innovations foster a mindset of continuous learning, experimentation, and adaptation. This adaptability becomes invaluable when dealing with disruptive changes in the market.
Market Resilience and Longevity
Companies that consistently engage in sustaining innovation are better equipped to navigate through economic downturns and market uncertainties. By keeping their products and services up-to-date, they can weather challenging times, maintain their market presence, and even win a larger market share.
Rather than being substitutes, sustaining and disruptive innovations are complementary forces that drive overall progress in an industry, coexisting and reinforcing each other in several ways.
Get Your Sustaining Innovation Demo →
The Apple Way
Apple Inc., with its iconic iPod and iPhone devices, is a prime example of a company that went down both the sustaining and disruptive roads to achieve resounding success. Through these groundbreaking products, Apple boldly targeted the core customers of entrenched incumbents and emerged victorious in highly competitive markets.
The iPod, when first introduced in 2001, can be considered both a sustaining and disruptive innovation, depending on the perspective and timeframe.
From a short-term perspective, the initial release of the iPod can be seen as a sustaining innovation. It represented an incremental improvement in the existing portable music player market. The concept of portable music players was not entirely new; various MP3 players and other portable devices were already available before the iPod’s launch. However, the iPod brought several enhancements to the table, such as its sleek design, user-friendly interface, and integration with iTunes software.
From a long-term perspective, the iPod can also be considered a disruptive innovation. While it initially targeted a niche market of music enthusiasts, its impact and transformative nature became evident over time. The iPod, along with the iTunes ecosystem, played a significant role in popularizing digital music and shifting the entire music industry’s landscape.
Similarly, in 2007, Apple unveiled the iPhone to disrupt the mobile phone industry. At that time, established players like Nokia, BlackBerry, and Motorola dominated the market with traditional cell phones, primarily focused on voice calls and text messaging. Apple recognized the untapped potential of a multifunctional device that combined a phone, music player, and Internet communicator.
Once again, Apple opted for the sustaining path, too, meticulously perfecting the iPhone’s design and functionality. The company invested in creating a sophisticated operating system, iOS, which provided a seamless and intuitive user experience. With each new iPhone release, Apple incorporated incremental improvements, such as better cameras, faster processors, and enhanced software capabilities, further solidifying its position as a leader in the smartphone market.
In both cases of the iPod and iPhone, Apple’s sustaining innovation not only secured its position as a market leader but also prompted its competitors to rethink their strategies and adapt to the changing market landscape. As the ripple effect of sustaining innovation spread across the industry, other players were forced to invest in their own research and development, leading to overall progress and advancement in the consumer electronics sector.
The Role of Culture and Leadership
According to a McKinsey survey, an overwhelming 94% of top executives named people and culture as the most critical drivers of innovation within an organization.
Building upon this insight, the global management consulting giant highlights the significance of three key people-management fundamentals as the foundation for cultivating an environment encouraging sustaining innovation and long-term growth.
While many companies acknowledge the significance of innovation, only a handful have truly embedded it into their long-term vision. By accomplishing this integration, innovation transforms into a central pillar of the company’s growth strategy, no longer a mere notion made in passing. Instead, it becomes subject to active management, diligent tracking, and rigorous measurement. This strategic alignment ensures that innovation gains the prominence it warrants, attracting the necessary attention and allocation of resources, resulting in more purposeful and influential initiatives.
Often, organizations hold a wealth of untapped creative capacity within their workforce. By fostering an environment conducive to the emergence and growth of dynamic innovation networks, employees are encouraged to collaborate, exchange ideas, and delve into novel solutions. Facilitating cross-functional collaboration and providing platforms for idea-sharing unlocks the hidden innovative potential of employees, allowing companies to tap into a wellspring of fresh ideas and creative problem-solving.
Nurturing an innovation culture built on trust among employees plays a pivotal role in sustaining innovation. In this empowering environment, employees feel confident expressing their ideas, knowing their contributions are genuinely valued and respected. Moreover, they perceive that taking risks and embracing experimentation is not only accepted but actively encouraged, with collective oversight provided by both peers and managers. As trust and open communication flourish, they become potent catalysts for innovation, fostering a seamless flow of ideas and knowledge.
Ultimately, an organization’s ability to innovate and adapt hinges on its people, making it imperative to invest in creating a supportive and empowering culture that fuels the spirit of innovation from within. Subscribing to an innovation management platform like InnovationCastⓇ is one example of such investment—regardless of whether you aim for disruptive innovations, sustaining innovations, or both.